Product line-up to increase the reliability of energy management and industrial equipment
Resistors
 Type
High Power Ceramic Insulation Fixed Resistors
Type
High Power Ceramic Insulation Fixed Resistors

(W)50

(W)80・120・220

(W)150・200・250・300・350・400

(W)60・80・100・120・150・200・250・300・400・500・750・1000

(W)750・1000・1200・1500

(W)100・150・200
(W)200・250・300・400・500
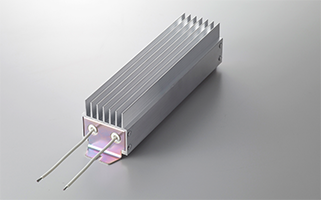
(W)300・400・500・600・700

(W)750・1000・1500・2000

(W)100・200
 Type
Metal Clad Wire Wound Fixed Resistors
Type
Metal Clad Wire Wound Fixed Resistors

(W)10・20・30・75・120・200

(W)6・8・10・30・50・75
 Type
Flame Proof Wire Wound Fixed Resistors
Type
Flame Proof Wire Wound Fixed Resistors

(W)5・10・20・30・40・50・60・80・100・120・150・200・250・300・400・500・750・1000

(W)3・5・10・15・20・22・25・35・43・50・66・88・108・130・168・210・315・420
 Type
Flame Proof Ribbon Wire Wound Fixed Resistors
Type
Flame Proof Ribbon Wire Wound Fixed Resistors
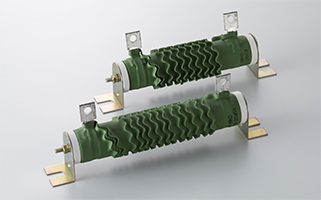
(W)90・120・150・180・225・300・375・450・600・750・1000・1300
 Type
Flame Proof Flat Wire Wound Fixed Resistors
Type
Flame Proof Flat Wire Wound Fixed Resistors

(W)21・31・53・68・91・150 (reference)・250 (reference)
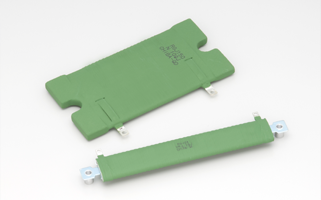
(W)15・22・37・47・63・150 (reference)・250 (reference)
 Type
Enclosed Wire Wound Variable Resistors
Type
Enclosed Wire Wound Variable Resistors
 Type
Flame Proof Wire Wound Variable Resistors
Type
Flame Proof Wire Wound Variable Resistors

(W)25・50・75

Standard Nominal Resistance Values
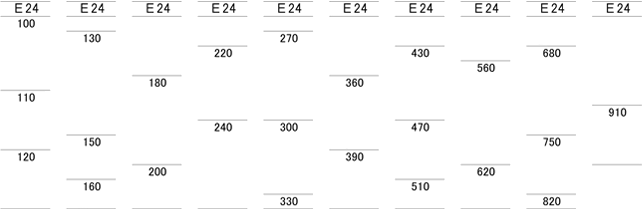
[Nominal Resistance Values]
Nominal resistance values fall into the series approximated using the following common ratio.

Glossary
[Ambient temperature]
Maximum value of the ambient temperature at which resistor can be continuously used with specified rated load (power) applied. Please note that this is the temperature around resistor inside the equipment where it is installed, not the air temperature outside the equipment.
[Power rating]
Maximum power that can be continuously applied to resistor at the rated ambient temperature.
[Voltage rating]
Maximum value of DC or AC voltage (effective value at commercial frequency) that can be applied continuously at the rated ambient temperature. It can be calculated by substituting the power rating and nominal resistance values to the following equation.
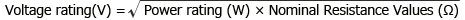
[Critical resistance]
Maximum nominal resistance to which the rated power can be applied without exceeding the maximum operating voltage. For the critical resistance, the values of rated and maximum operating voltage are the same.
[Maximum operating voltage]
Maximum value of DC or AC voltage (effective value at commercial frequency) that can be applied continuously to a resistor or resistive element. However, for resistance values below the critical resistance, the maximum applied voltage must not exceed the rated voltage.
[Maximum load voltage]
The maximum applicable voltage in the overload test (JIS C 5201-1 4.13).
[Withstanding voltage]
AC voltage (effective value at commercial frequency) that can be applied for 1 minute between terminals and designated point on the housing in the withstand voltage test (JIS C 5201-1 4.7).
[Derating curve]
Curve expressing the relationship between the ambient temperature and maximum power that can be loaded continuously at that temperature. Generally expressed as percentage.
[Temperature coefficient of resistance]
The rate of resistance change per 1°C between specified temperatures within the operating temperature range of resistor, which is expressed by the following equation.

Usage notes
1. Handling precautions
Please be especially careful when using resistors in the following environmental conditions.
- 1) When using in water, organic solvents and other liquids.
- 2) When using in places with large concentration of SO2, NO2 and other corrosive gases.
- 3) When using embedded in resin, with coating applied, etc.
- 4) When using water and water-soluble detergents during flux cleaning.
- 5) When using in places where condensation may occur.
2. Storage
Since long-term storage may lead to resistor performance deterioration, please be careful when storing products in the following environment.
- 1) In places with high temperature, high humidity and direct sunlight.
- 2) In places with high concentration of corrosive gases.
- 3) It is recommended to use products within 6 months after delivery.
3. Pulse withstanding properties
Please be especially careful when using resistors in circuits with high voltage pulses and surge currents.